Health vs Heritage: Pigeon Feeding Ban Sparks Debate in India
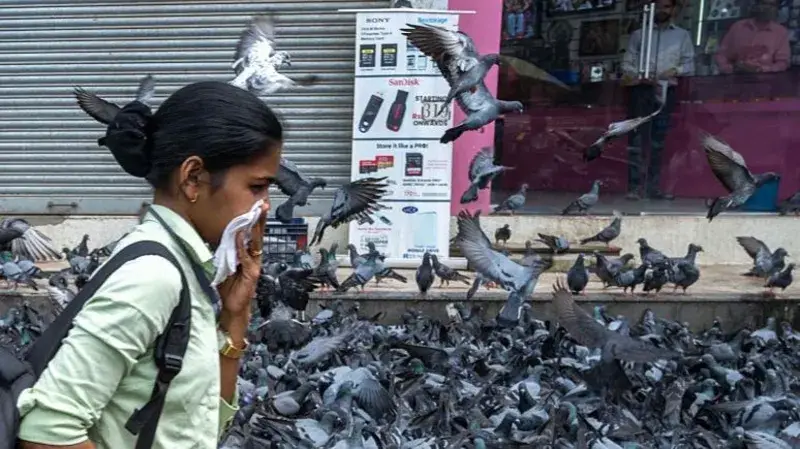
In India, a new controversy is stirring across cities: the ban on pigeon feeding. For generations, feeding pigeons has been regarded as an act of kindness, faith, and tradition. However, authorities and health experts now warn that the growing pigeon population is becoming a serious public health risk. This clash between health concerns and cultural heritage has sparked heated debates in India.
Why Is Pigeon Feeding Being Banned?
Pigeon feeding, common in temples, markets, and busy chowks, has long been considered an act of charity in Indian society. But recent medical studies and government advisories highlight the dangers:
- Health Risks: Pigeon droppings are known carriers of fungi and bacteria, which can cause respiratory diseases such as hypersensitivity pneumonitis (commonly called “pigeon breeder’s lung”).
- Allergies and Asthma: Doctors in major Indian cities report a rise in allergy and asthma cases linked to pigeon droppings and feathers.
- Urban Nuisance: Pigeons breed rapidly, and uncontrolled feeding has led to overpopulation in crowded city areas, damaging monuments, vehicles, and public spaces.
As a result, civic bodies in cities like Mumbai, Ahmedabad, and Jaipur have started imposing restrictions on feeding pigeons in public places.
The Cultural and Religious Angle
For centuries, feeding pigeons has been a deeply symbolic tradition in India. Many communities see it as an act of compassion and good karma, while others associate it with religious rituals. In Hinduism and Jainism, feeding birds is often linked to earning merit and showing respect for nature.
Supporters of the practice argue that banning pigeon feeding is an attack on culture and faith. They believe that instead of outright bans, authorities should promote cleaner and safer feeding zones.
The Ongoing Debate
The “Health vs Heritage” debate is dividing opinion:
- Supporters of the Ban say protecting public health should come first. With rising cases of respiratory illnesses in India’s cities, they argue that controlling pigeon populations is necessary.
- Opponents of the Ban argue that traditions should not be discarded. They believe with better planning—such as designated feeding areas or pigeon shelters—India can preserve culture while reducing risks.
Finding a Middle Ground
Experts suggest that the solution lies not in extreme bans, but in regulated practices:
- Creating designated pigeon feeding zones away from crowded residential areas.
- Running awareness campaigns about the health risks of overfeeding pigeons.
- Promoting eco-friendly urban planning that balances heritage with hygiene.
Conclusion
The pigeon feeding ban in India is more than a civic issue—it’s a reflection of the country’s ongoing struggle to balance tradition with modern health concerns. While authorities stress on safeguarding citizens from health risks, communities emphasize the need to preserve cultural practices. The debate continues, but what’s clear is that India must find a practical middle path that respects both health and heritage.
✅ SEO Keywords to target: pigeon feeding ban India, health vs heritage India, pigeon health risks, Indian traditions, respiratory diseases from pigeons, pigeon overpopulation India